Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) is a framework containing a set of best practices for delivering efficient IT Support services. ITIL enables individuals and organizations to deliver cost-effective IT Service Management and companies adopt ITIL in order to realize their business benefits faster with defined processes. ITIL focuses on resource optimization and regularly reviewing the existing processes in order to gain improvement. It is also capable of acting as a business partner for organizations to adopt only those practices that are applicable to them.
An ITIL process owner ensures that the ITIL process generates the desired outcomes in a manner such that it serves in the best interest of the organization. If an ITIL process does not fulfill its purpose, corrective actions should be activated in order to obtain the desired results. It is the duty of the ITIL process owner to guarantee that these corrective actions are taken by the individual in the relevant role. The ITIL process owner thus plays a very important role in ensuring that an ITIL process runs in a smooth and efficient manner. Following are some of the key tasks of an ITIL process owner:
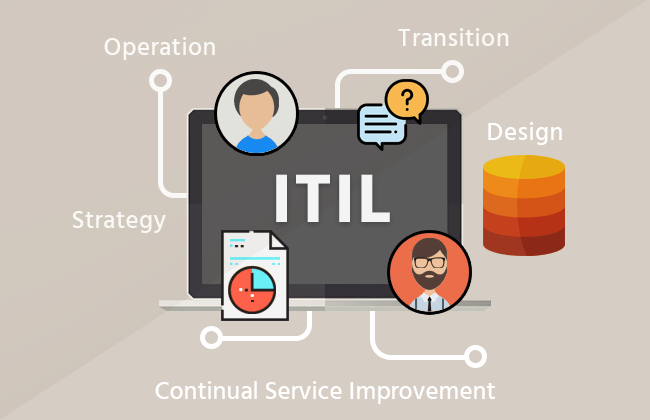
There are 5 stages of the ITIL lifecycle and it is extremely essential for the IT service manager to be aware of each ITIL process and for the service owner to understand how to implement each of the stages’ processes as he/she ultimately takes ownership of the service and its lifecycle.
Stage 1: Service Strategy
This is the core stage of the ITIL service lifecycle. An IT service will succeed only if a solid IT strategy is aligned with the organization’s business strategies. The ITIL process followed in this stage makes way for all the other stages possible and also provides direction for the stages that follow.
Stage 2: Service Design
The planning and design activities of IT strategies are executed in this stage. Ideas are generated based on the inspiration drawn from IT strategies, be it updates on existing services or new services. The planning and designing of new services in this stage help achieve the business vision and strategy of the organization. This stage also includes service level management, capacity management, service catalog management, service continuity management, information security management, supplier management processes, and availability management. It is necessary for the IT service owner to be familiar with all these processes and efficiently manage the ITIL process by getting guidance from the IT service manager.
Stage 3: Service Transition
In this stage, designed new services or changed services are built, tested, implemented, proved and transferred into operations. This Service Transition stage in the ITIL process is considered to be the key step during which an idea is planted in soil (just like a seed) and it is allowed to grow to fruition. This stage deals with service assets and configuration management, transition planning and support, change management, service validation and testing evaluation, knowledge management processes, and release and deployment management. Change management is particularly important if an existing service is being altered.
Stage 4: Service Operation
This fourth stage in the ITIL process is one in which designed services are put into a live environment and end customers begin to use services of the organization. The service will probably delight the customer and also succeed as a service if each ITIL process were accurately followed. This stage includes incident management, request fulfillment, event management, access management processes, and problem management. An ITIL process that is ignored in this stage will result in customers getting disappointed, thus leading to loss of sales.
Stage 5: Continual Service Improvement (CSI)
This final stage in the ITIL process brings together all the four service lifecycle stages and focuses on identifying and examining the improvement points in these stages. This is followed by implementing the enhancement plans in order to mitigate any points of pain in the processes. This stage includes service reporting, service measurement, 7 Step improvement process, return on investment for CSI, service level management processes, and the business questions for CSI. The CSI process is considered to be the shell capable of protecting each ITIL process. A service with longevity in the market can be obtained with the effective usage of efficient CSI processes.
Conclusion
If a service has to be successful, proper IT Service management should be executed throughout the service lifecycle. There are a number of processes to be designed, optimized and followed, each related to a particular step in the ITIL service lifecycle. It is essential for one to understand the fact that a poor ITIL process or processes that are incorrectly followed can easily cause damage that could eventually lead to customer dissatisfaction.
How to find Android Device Manager on my Phone?
CRM Software for Your Small Businesses
Artificial Intelligence can Transform your Small Business
Add new comment